Dust Modelling
Modelling dust attenuation in galaxy SEDs
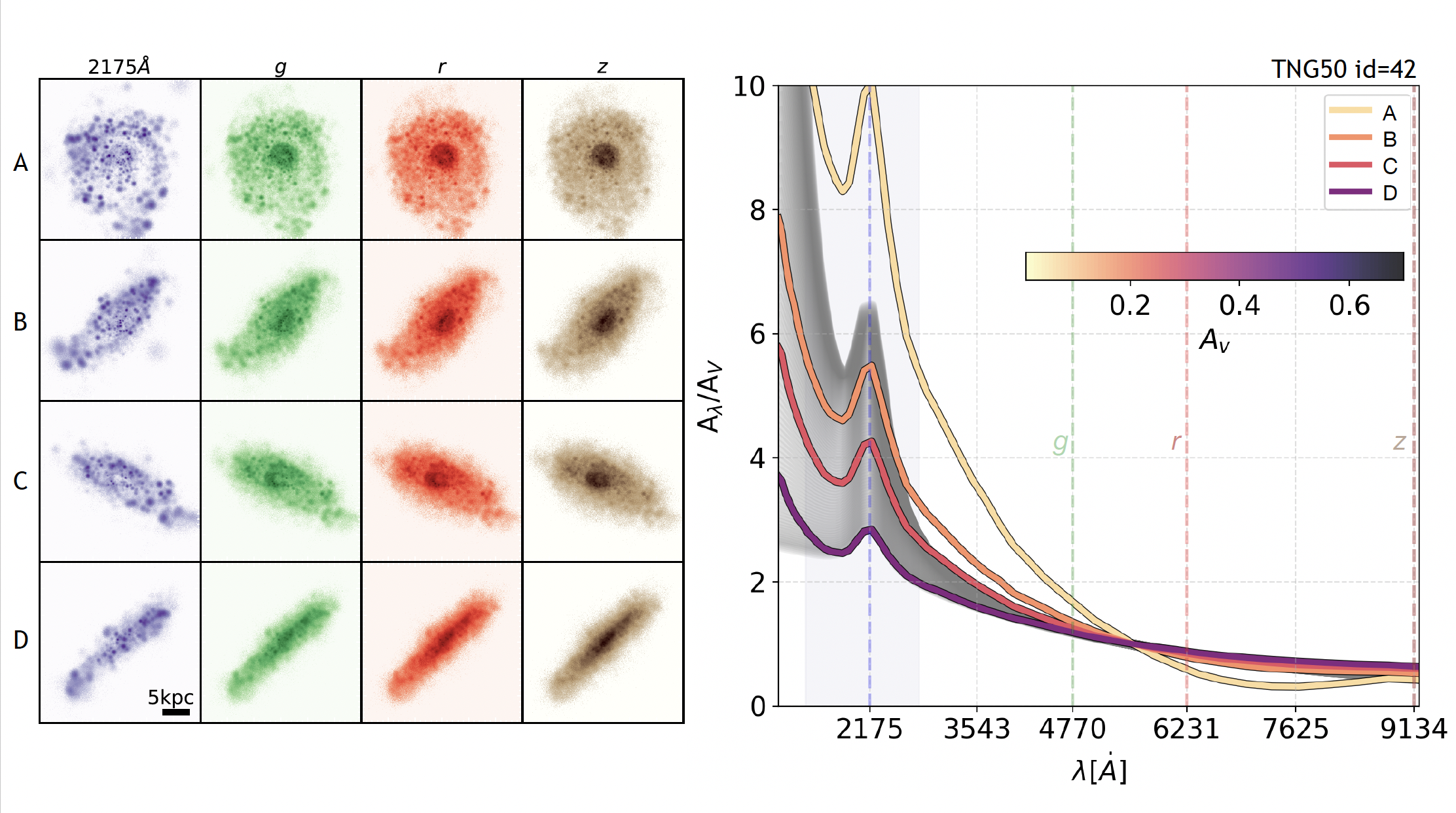
We have performed radiative transfer post-processing on ∼6400 galaxies from the TNG50 simulation—each viewed along 51 lines of sight—using SKIRT to study the impact of dust attenuation on galaxy SEDs. Based on these results, we developed a simulation-informed analytic model for attenuation curves, described by a minimal set of scaling relations tied to fundamental galaxy properties. This compact, predictive model is designed for integration into tools like Synthesizer and CAMELS-SAM, enabling efficient forward modeling of dust attenuation in SED fitting and inference studies.
The first paper from this project (Sommovigo et al., 2025) has been accepted for publication and was part of the collaboration Splash. Future work will explore model extensions and integration into the LtU Implicit Likelihood Inference pipeline to evaluate the impact of marginalizing over dust-related uncertainties in cosmological inference.
As a follow-up, we are also developing machine learning techniques to compress the dimensionality of attenuation curves using Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Informed Bottleneck (IOB) analysis. These methods aim to extract physically meaningful features and establish direct links between attenuation curve variations and galaxy properties through regression models developed by the ILI group.
References
2025
- arXiv e-prints, Feb 2025