Information-Ordered Bottleneck
Adaptive, ordered compression for interpretable neural networks
Deep neural networks (DNNs) have revolutionized data analysis across numerous fields, offering powerful tools to uncover complex patterns in high-dimensional datasets. However, their computational demands, lack of interpretability, and risk of overfitting pose significant challenges. To address these issues, we introduce the information-ordered bottleneck (IOB) (Ho et al., 2023), a neural layer designed to compress and order latent variables by their importance in minimizing the likelihood.
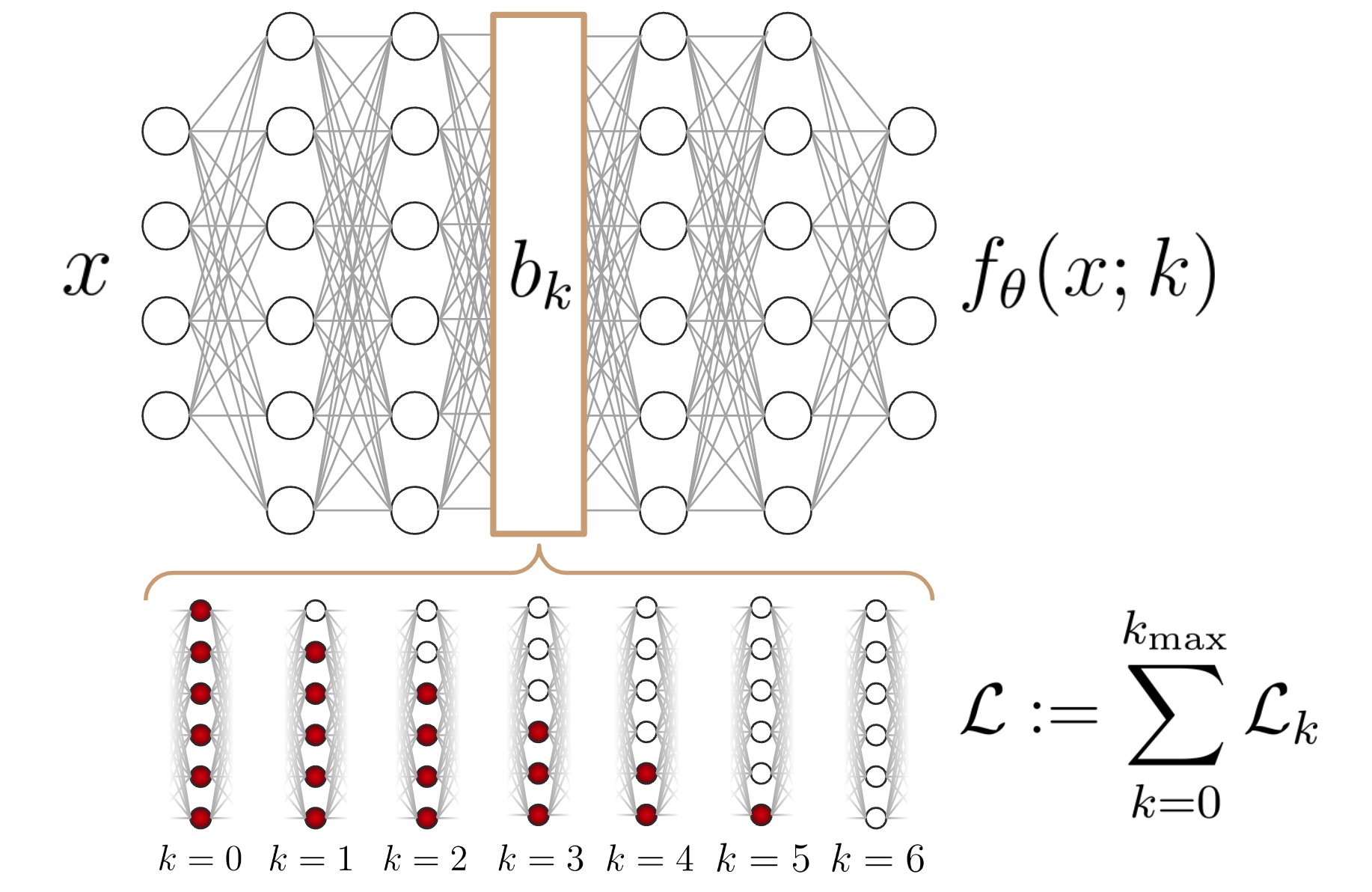
The key idea behind this approach is we vary the width of the DNN bottleneck during training, encouraging the neural network to pass the most important information through the most reliable neurons (i.e. those at the top). This layer is integrable into many exotic neural architectures, allowing for ordered compression in many machine learning tasks.
As an example, we below show the result of image compression in an autoencoder architecture, using an IOB architecture and using classical linear PCA. Each image is defined by two disks of different radii and xy-positions, characterizing a six-dimensional latent space.
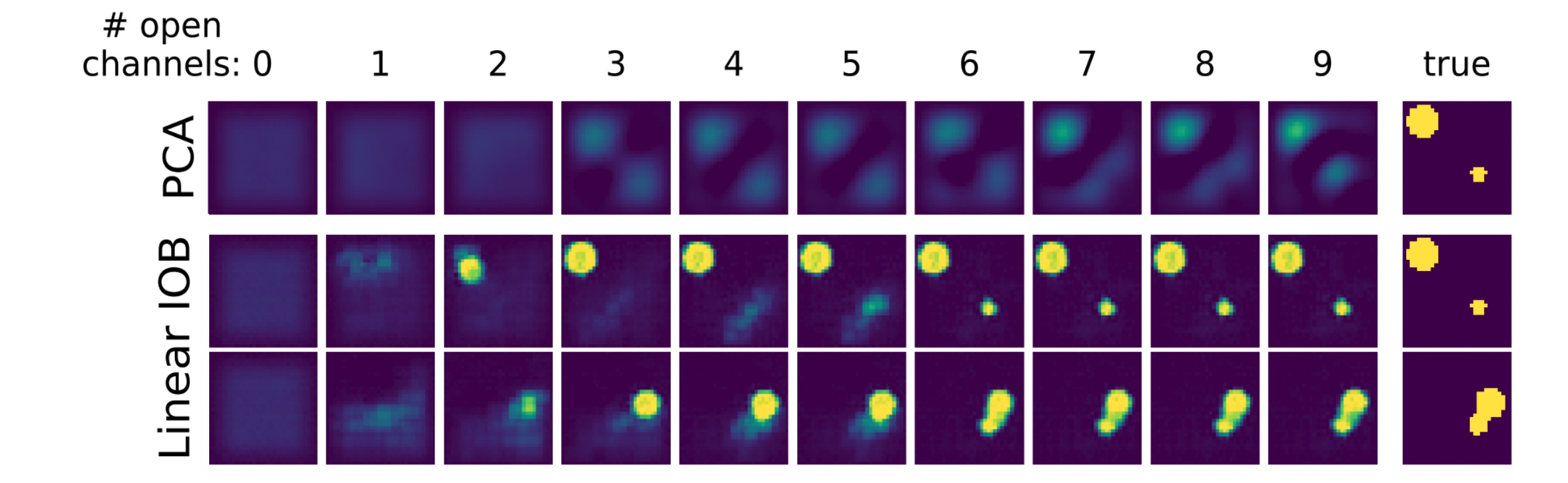
As shown here, the IOB architecture is able to reconstruct the images with significantly less latent variables than PCA. In fact, we observe that the image reconstruction requires about six variables, exactly equal to the number of parameters characterizing the dataset.
This core feature of IOBs is their ability to estimate intrinsic dimensionality (ID)—the minimal number of variables required to represent the underlying structure of a dataset. By leveraging a likelihood-based methodology, IOBs provide a robust tool for analyzing latent spaces, offering insights into data complexity and guiding model design. This capability is particularly valuable for datasets where the underlying relationships are nonlinear or heterogeneous, as it allows for efficient compression while maintaining interpretability. IOBs unify and extend prior approaches, demonstrating their utility as a generalized solution for embedding data in a hierarchical and semantically meaningful manner.