Mistral
A BH feedback subgrid model for AGN-driven winds
When actively accreting matter, supermassive black holes (SMBHs) in active galactic nuclei (AGN) can launch powerful winds, driving high-velocity outflows that can extend to galactic scales. These broad-line and nuclear winds are powered by radiatively efficient accretion processes, which occur on small scales typically unresolved in large-scale cosmological simulations. To account for this limitation, AGN feedback has traditionally been modelled using subgrid prescriptions, and, in the radiatively efficient regime of SMBHs, most often as continuous thermal energy injection. However, it remains uncertain whether such models can reliably reproduce large-scale gaseous outflows as observed out to redshift z = 7.5. As an alternative approach, Mistral is a subgrid model for AGN-driven winds, designed to capture their impact on SMBH and galaxy evolution by modelling the transfer of mass, momentum and energy into the surrounding interstellar and circumgalactic medium.
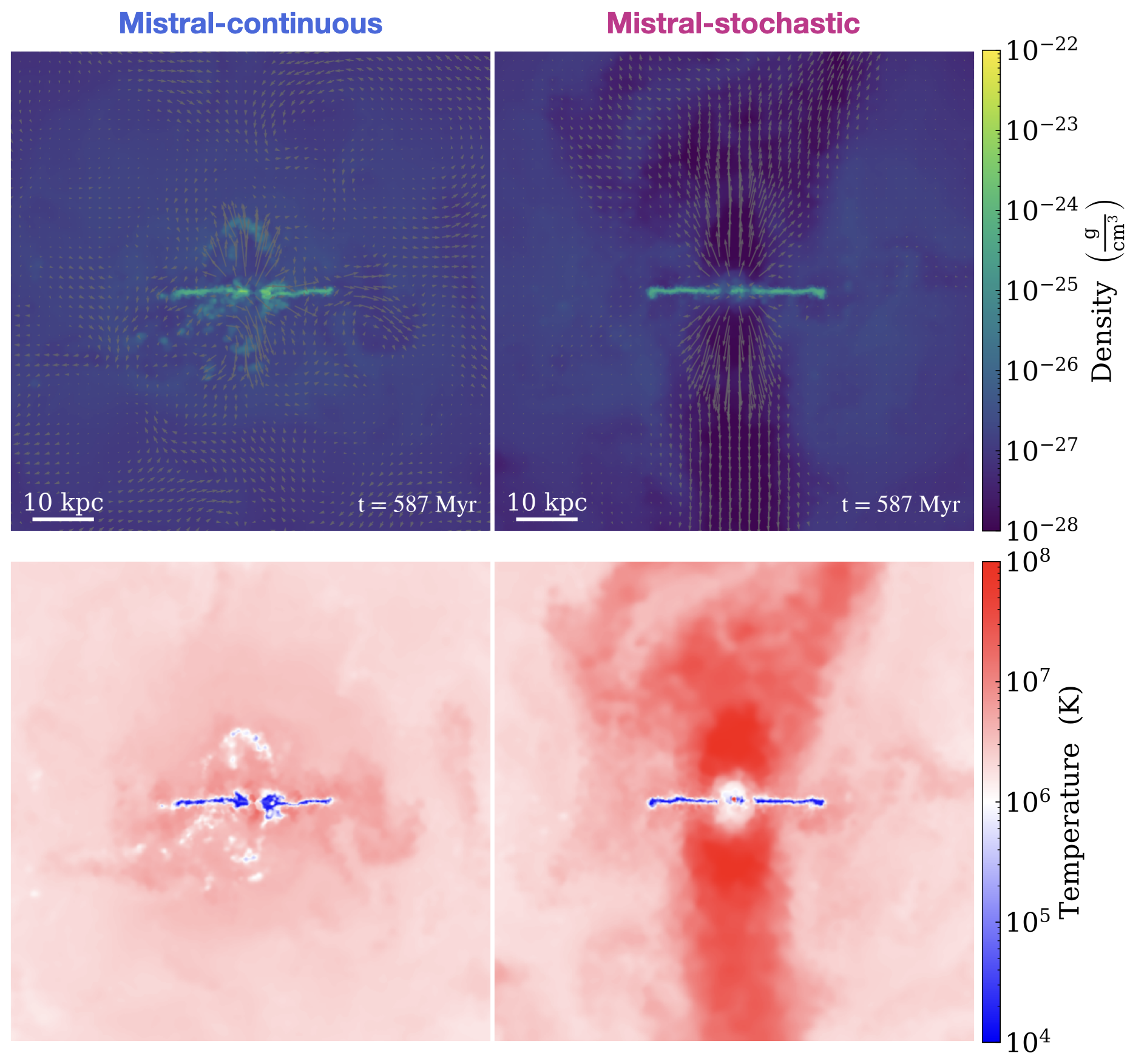
In (Farcy et al., 2025), we detail the Mistral framework and explore two variants of our implementation: continuous radial deposition of momentum (Mistral-continuous), and stochastic bipolar momentum injection (Mistral-stochastic). The latter, which is the fiducial Mistral model, is the Arepo (Springel 2012) analogue of the model implemented by Choi et al. 2012 in the Gadget code (Springel 2005). In this first paper, we investigate the effect of Mistral on BH and galaxy properties using an idealized Milky Way-mass galaxy and cosmological zoom-in simulations down to z=2. In forthcoming work, we will explore the role of AGN winds modelled with Mistral in shaping high-redshift galaxies and quasars, aiming to interpret the growing number of JWST observations. Additionally, a companion study will assess the ability of Mistral to produce AGN-driven X-ray cavities in massive galaxies at z=0.1-0 (see also the dedicated project page).